The-Strategic-Impo-tance-of-the Gaza-Strip-to-Israel-and-Middle-Eastern-Countries
The Strategic Importance of the Gaza Strip to Israel and Middle Eastern Countries
Dave Ikiedei Asei
October 18, 2024
The Gaza Strip, a narrow stretch of land along the eastern Mediterranean coast, is a highly contested and politically sensitive region in the Middle East. Though relatively small, its strategic location, political significance, and socio-economic dynamics give it an outsized influence on the regional and global stage. This article delves into the strategic importance of the Gaza Strip for Israel and other countries in the Middle East, highlighting its geographical, political, and military significance.
Geographical Importance
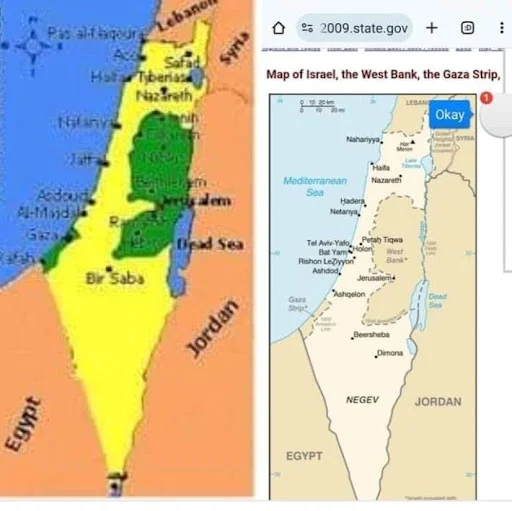
The Gaza Strip is a coastal enclave located between Israel and Egypt, with a 41 km coastline on the Mediterranean Sea. Its geographical positioning makes it a key area for several strategic reasons.
Access to the Mediterranean Sea: For Israel, control over the Gaza Strip or, at the very least, maintaining a security buffer around it is crucial. The Mediterranean Sea is a vital shipping route for trade, energy transportation, and military maneuvers. Any disruptions to maritime traffic in this region could have direct economic and security implications for Israel and neighboring states.
Proximity to Key Players: The Gaza Strip is geographically close to several key players in the Middle East, including Israel, Egypt, and the broader Arab world. Its proximity to Israel’s major cities like Tel Aviv and Ashdod, as well as to Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula, makes it a critical flashpoint. Control or influence over Gaza offers potential leverage over these nations’ security, commerce, and diplomacy.
Border Security and Control: Gaza's borders with Israel and Egypt are crucial points for managing regional stability. For Israel, securing the border with Gaza is necessary to prevent militant groups from launching attacks, while Egypt sees the Gaza-Egypt border as a key area for controlling smuggling, human trafficking, and terrorism from spreading into the Sinai Peninsula.
Political and Diplomatic Significance
The Gaza Strip holds immense political significance not only for Israel and Palestine but also for the broader Arab and Muslim world.
Israel-Palestine Conflict: The Gaza Strip is a central issue in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. As the home base of Hamas, an Islamist militant organization that controls the territory, Gaza represents both a physical and symbolic battleground in the broader struggle for Palestinian statehood. For Israel, ensuring its security involves managing tensions with Hamas, and by extension, its relations with other Palestinian groups in the West Bank and the wider Arab world.
Arab and Islamic Unity: Gaza plays a symbolic role in the broader Arab-Israeli conflict. Arab and Muslim countries often view the Palestinian struggle, particularly the situation in Gaza, as a rallying point for their foreign policies. Countries like Iran, Turkey, and Qatar have provided material and political support to groups in Gaza, especially Hamas, as part of their broader efforts to challenge Israel and increase their influence in the region. Iran, in particular, views its support for Gaza as part of its "resistance axis" against Israel and the U.S.-backed regional order.
International Diplomacy: The situation in Gaza continues to attract global attention, often serving as a flashpoint for international diplomatic efforts. The recurring conflict and humanitarian crises in Gaza lead to interventions from the United Nations, European Union, and other global actors. The U.S., which is a key ally of Israel, is often involved in brokering ceasefires or providing military and economic support to Israel in its efforts to manage the security risks emanating from Gaza. Thus, Gaza remains a focal point of international diplomacy in the region.
Military and Security Considerations
From a military and security perspective, the Gaza Strip is highly significant for Israel and its neighbors, owing to the ongoing conflict between Israel and Hamas.
Terrorist Threats: Gaza is a base of operations for various militant organizations, including Hamas and Islamic Jihad, both of which pose a direct threat to Israeli security. Over the years, these groups have used Gaza as a launchpad for rocket attacks, tunnels for smuggling and infiltration, and other forms of asymmetrical warfare. Israel, in turn, has invested heavily in defense systems like the Iron Dome to intercept rockets and has launched multiple military operations in Gaza to neutralize these threats.
Border Tensions and Blockades: Israel maintains a tight blockade around Gaza, controlling what goods and people can enter and leave the territory. This blockade is aimed at limiting Hamas’ access to weapons, but it has also led to significant humanitarian concerns. Meanwhile, Egypt’s border with Gaza is also tightly controlled, with occasional openings for humanitarian reasons. Both Israel and Egypt face the challenge of balancing security concerns with the needs of the civilian population in Gaza.
Regional Security Dynamics: The security situation in Gaza influences broader regional security dynamics. Egypt is particularly concerned about the spread of extremism and instability from Gaza into the Sinai Peninsula, which has already been a hotbed of insurgent activity. Similarly, Israel’s security measures in Gaza have implications for its relations with other countries in the region, including Jordan and Lebanon, where Hezbollah, another Iran-backed militant group, operates.
Socio-Economic and Humanitarian Considerations
Beyond its strategic military and political significance, Gaza also holds socio-economic and humanitarian importance for Israel and neighboring countries.
Humanitarian Crisis: Gaza is one of the most densely populated areas in the world, with over two million people living in a small, confined area. Years of conflict, blockades, and restricted access to resources have led to severe humanitarian challenges, including shortages of food, clean water, and medical supplies. Humanitarian organizations often highlight the situation in Gaza as a pressing global concern. Israel and Egypt, while prioritizing security, also face international pressure to ease the conditions in Gaza to avoid worsening the humanitarian crisis.
Economic Interdependence: Although Gaza’s economy is largely isolated due to blockades, there remains a degree of economic interdependence between Gaza and Israel. Israel supplies Gaza with electricity, fuel, and some consumer goods, though the flow is heavily regulated. A more peaceful and stable Gaza could present economic opportunities, including trade and investment, for both Israel and Egypt, especially in industries like construction, infrastructure, and agriculture.
International Aid: Many countries and international organizations provide humanitarian and financial aid to Gaza, often as part of broader efforts to alleviate the conflict. This aid plays a role in stabilizing the region and preventing further radicalization or collapse, which could lead to greater security threats. Countries like Qatar have been key players in providing financial assistance, while the European Union and the United Nations are involved in humanitarian efforts.
Conclusion
The Gaza Strip is a strategically significant region for Israel and other Middle Eastern countries, with its importance extending beyond its small geographical size. Its proximity to Israel and Egypt, the presence of militant groups, and its role in the broader Israeli-Palestinian conflict make it a central issue in regional security and diplomacy. Additionally, the humanitarian situation in Gaza continues to attract international attention, highlighting the complex interplay of security, politics, and human rights in the region. For Israel, maintaining security in and around Gaza is critical to its national defense, while for other Middle Eastern countries, Gaza represents both a challenge and a focal point for broader geopolitical maneuvering.




Comments